Dead tooth: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
September 30, 2020A tooth is referred to as ‘dead’ when it no longer has any blood flow. Sometimes this is also called as a ‘non-vital tooth.’
Tooth decay and an injury both can cause a dead tooth. In this blog, we will look at the causes and how a dead tooth can be treated and prevented.
What causes a tooth to die?
- Trauma or injury to your tooth or mouth is one possible cause for a dead tooth.
- A tooth can also die as a result of poor oral hygiene, leading to cavities, which, when left untreated, can gradually destroy your tooth.
Dead Tooth Treatment
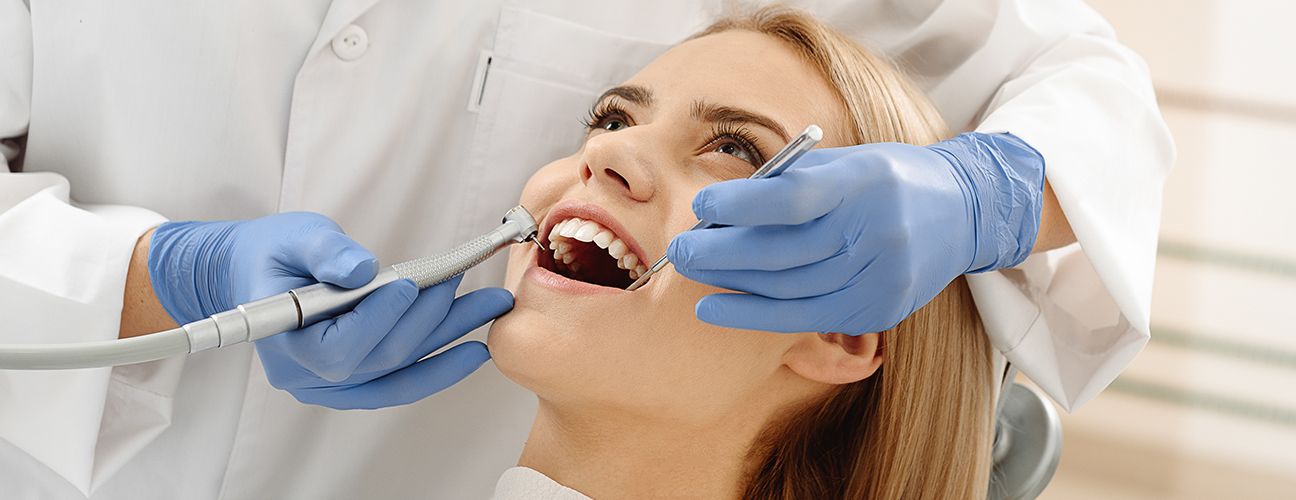
It is important to treat a dying or dead tooth as soon as possible. That is because if left untreated, the bacteria from the dead tooth can spread and lead to the loss of more teeth. Moreover, it could hit your gums and jawbone.
Your dentist may treat a tooth that is dead or dying with a procedure known as a root canal. Or, they may extract the entire tooth.
Root canal
With a root canal procedure, you may be able to keep your tooth intact. During the root canal, the dentist drills an opening into the tooth and then uses small instruments to remove the pulp and clean out the infection. Following the infection removal, your dentist will place a permanent filling and seal the roots.
In many cases, your doctor may recommend having a crown after a root canal. This may be a good option if there was damage to the enamel or if the tooth had a large filling.
If your dentist or endodontist determines that you don’t need a crown, you may be able to use tooth bleaching to treat any color changes to the affected tooth. If not, your doctor may recommend covering the tooth with a porcelain veneer.
Removal or extraction
If your tooth is badly damaged and unable to be restored, your dentist may recommend removing the dead tooth completely. During the procedure, the dental professional will completely remove the tooth. After the extraction, you can replace the tooth with a denture, implant, or bridge. Talk to your dentist or oral surgeon about your options. Some questions you should ask are:
- What is the recovery like?
- How much will it cost?
- Will it need to be changed over time?
Pain management
If your tooth is causing intense pain, there are some things you can do at home while you wait for treatment:
- Avoid hot beverages. They can aggravate inflammation, which can make your pain worse.
- Take an OTC anti-inflammatory medication, like ibuprofen.
- Avoid eating hard snacks. The biting-down force may worsen the damaged nerves.
It is best in your interest to visit your dentist immediately. Home remedies should not be used in place of professional treatment. Instead, you should use them while you wait for your dental appointment.